是一点 selection algorithm
支持随机查找的数组中找到第k大的元素是只需要线性时间. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Median_of_medians
c++标准库里面也有类似的算法, std::nth_element
但是他没有返回值, 而是把有random access iterator的容器的元素顺序改变了, 保证比第n个元素大的都在第n个元素前面,第n个元素就是第n小的元素. 听起来过程和 median of medians 差不多一样, 此时我还不知道intro sort这种东西… 于是准备写一个比 nth_element 更快的模板, 有返回值, 不改原来的序列的元素.
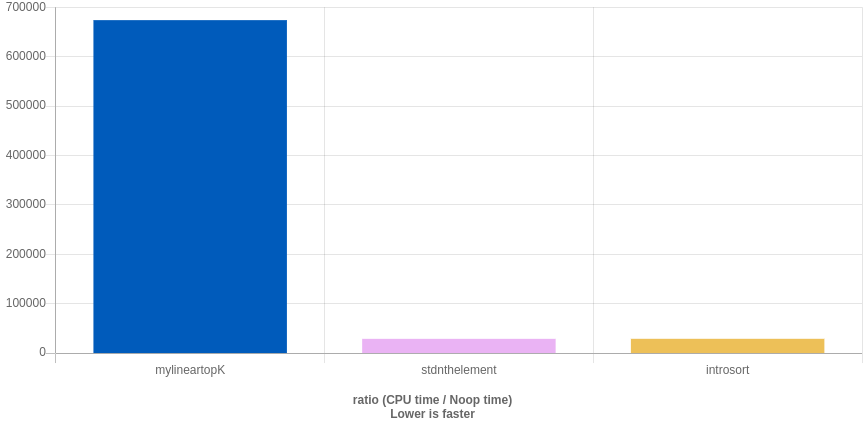
然后…成功成为小丑, 维基百科的 median of medians 抄下来比标准库慢好多…
median of medians 是把元素五个一组(一个 5-tuple)找中位数,
然后找到中位数的中位数(pivot). 现在有一半的tuple的中位数小于pivot,
每个tuple都有五个元素, 其中两个小于这个tuple的中位数,
两个大于这个tuple的中位数. 这样我们就知道了,
在tuple的中位数小于pivot的这些tuple里面,
小于等于该tuple中位数的元素(每个tuple有三个这样的元素)都一定小于pivot.
也就是说如果我们把\(\lceil \frac{n}{5}
\rceil\)个tuple都按照他们的中位数大小关系排好序的话,
排在pivot所在的tuple前面的这些tuple里面,有60%是一定比pivot小的,
他们一定是前半个序列的前60%的元素,
同理排在pivot所在tuple后面的所有tuple,
每个都有三个元素比pivot大,他们一定位于后半序列的最后60%,
我们每次至少可以扔掉50%*60%=30%的元素(这是最坏情况,
pivot所在tuple经过排序之后恰好在第一个或最后一个, 实际上我们不排序!)
注意到选择pivot仍然是一个select过程, 我们一样可以用这个median of
median来做, 非常巧妙
\[ T(n)=T(n/5)+T(0.7n)+O(n) \]
然后再来看看introsort是怎么做的
这是stl_algo.h的实现
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Size, typename _Compare>
_GLIBCXX20_CONSTEXPR
void
__introselect(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __nth,
_RandomAccessIterator __last, _Size __depth_limit,
_Compare __comp)
{
while (__last - __first > 3)
{
if (__depth_limit == 0)
{
std::__heap_select(__first, __nth + 1, __last, __comp);
// Place the nth largest element in its final position.
std::iter_swap(__first, __nth);
return;
}
--__depth_limit;
_RandomAccessIterator __cut =
std::__unguarded_partition_pivot(__first, __last, __comp);
if (__cut <= __nth)
__first = __cut;
else
__last = __cut;
}
std::__insertion_sort(__first, __last, __comp);
}introsort基本上就是quicksort的pivot划分过程+heap sort+insertion sort
但是stl是没有用插入排序的, 而且很多地方在语言上做了优化. 基本上还是一样的.
首先在list比较大的时候递归调用introsort,
首先用std::__unguarded_partition_pivot找个pivot,
方法是直接取当前序列的正中间的元素作为pivot. 然后根据要找的
nth_element和pivot相比哪个大来修改下一步递归的区间.
在list比较小的时候就直接用heap select, 这个函数是这样的:
/// This is a helper function for the sort routines.
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
_GLIBCXX20_CONSTEXPR
void
__heap_select(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_RandomAccessIterator __middle,
_RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp)
{
std::__make_heap(__first, __middle, __comp);
for (_RandomAccessIterator __i = __middle; __i < __last; ++__i)
if (__comp(__i, __first))
std::__pop_heap(__first, __middle, __i, __comp);
}先建堆, 然后满足条件就pop
make_heap
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
_GLIBCXX20_CONSTEXPR
void
__make_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last,
_Compare& __comp)
{
typedef typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::value_type
_ValueType;
typedef typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::difference_type
_DistanceType;
if (__last - __first < 2)
return;
const _DistanceType __len = __last - __first;
_DistanceType __parent = (__len - 2) / 2;
while (true)
{
_ValueType __value = _GLIBCXX_MOVE(*(__first + __parent));
std::__adjust_heap(__first, __parent, __len, _GLIBCXX_MOVE(__value),
__comp);
if (__parent == 0)
return;
__parent--;
}
}_GLIBCXX_MOVE std::move,
所有的临时变量都用右值引用存起来, 少了很多复制操作
我好慢…